When lung cancer cells spread to other parts of the body, the new tumors they form there are made of lung cells. So, even if this new tumor is in the liver, bones, or brain, it will still be called a lung cancer.
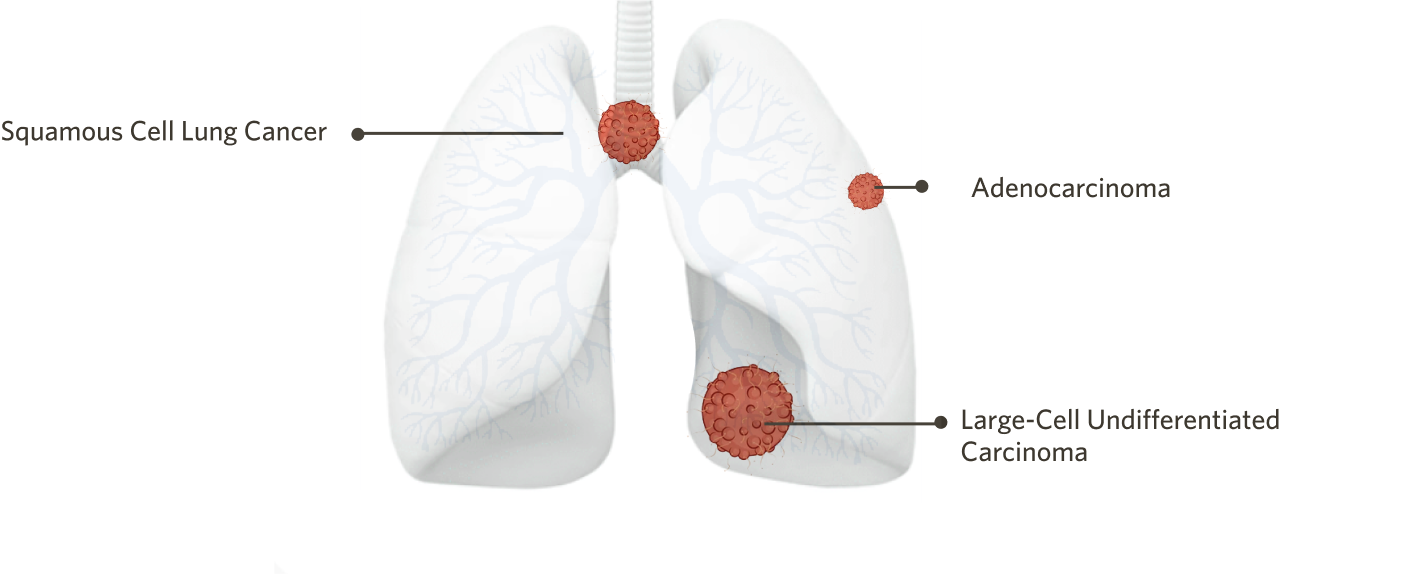
About 10-15% of all lung cancers are small cell lung cancer (SCLC), which is sometimes called oat cell cancer. This type of lung cancer tends to grow and spread faster than non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). About 70% of people with SCLC have cancer that has already spread at the time they are diagnosed. This cancer initially responds to chemotherapy and radiation therapy, but unfortunately, the cancer eventually returns in most people.
Not all tumorous growths in the lungs are necessarily cancerous. A lung mass, also called a nodule, is a small abnormal area that can be found during a 3D X-ray or Computed Tomography (CT) scan of the chest. These scans are often done as part of lung cancer screening. Most lung nodules seen on CT scans are not cancer. Sometimes, they’re the result of old infections or scar tissue. As a result, additional tests are often needed to be sure a nodule is not cancer.
Many people have small masses of tissue in their lungs. These small masses are called nodules. A nodule may have been found in your lung by chance.
Since there are very few nerves in your lungs, nodules often don’t cause symptoms. They are often found by chance on X-rays for an unrelated health problem. On X-rays, nodules may be called spots or shadows. Nodules can be caused by cancer, infections, scar tissue, or other health conditions. Most nodules are not cancer, but it takes a team of experts to determine if a nodule is cancer.
To decide if a nodule is cancer your doctors may:
Assess your risk for lung cancer Review images for signs of cancer Perform follow-up imaging Perform a procedure called a needle biopsy
Stopping
your
smoking habit is important. When you do, studies have shown it can: Increase your
lifespan
even if
the cancer has spread. Lower the
chances of getting
another lung cancer. Lower the high
risk of getting
other cancers and other diseases. If
you want more information
about smoking cessation, talk to your doctor or call the
American Cancer Society at 800-227-2345. City
of Hope’s C31 Cessation Program
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Repeated lung infections
- Coughing up blood
- Wheezing
- Sudden weight loss
- Tiredness
- Others
Show All
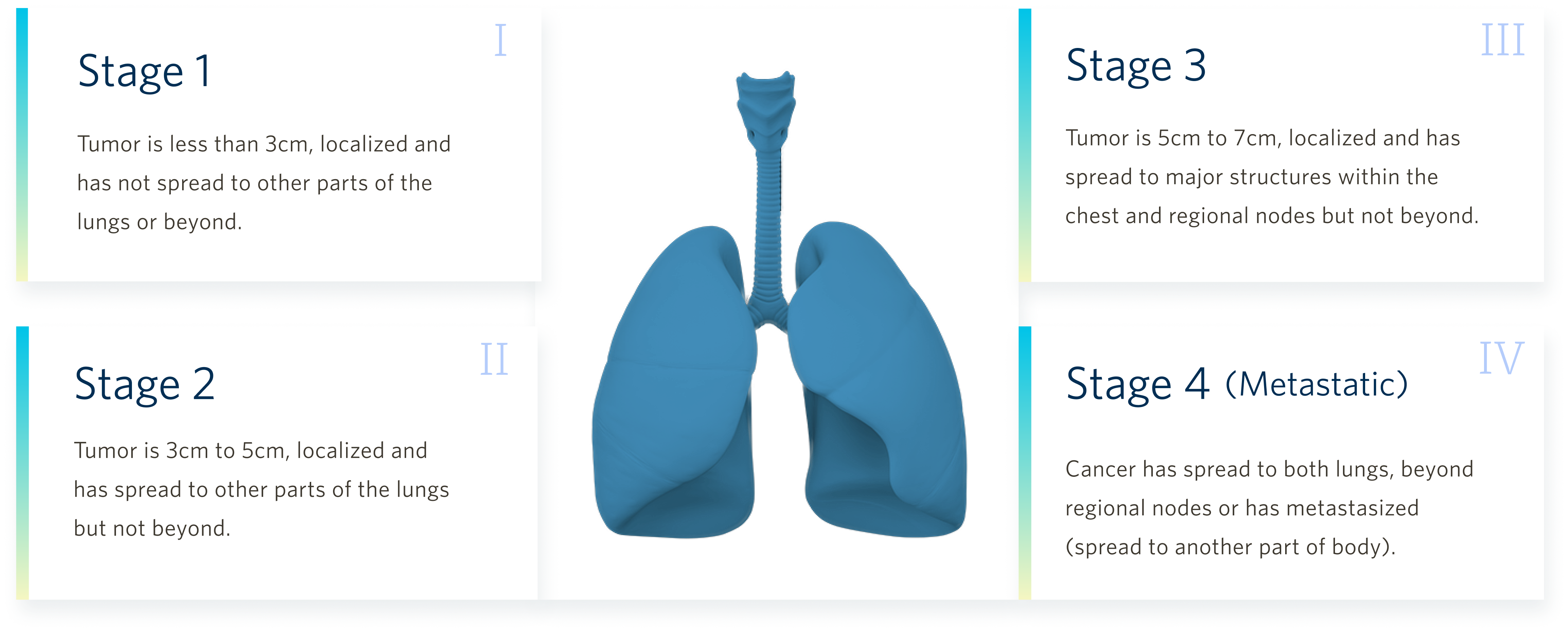 For
additional information regarding staging, please click here.
For
additional information regarding staging, please click here.